Cervical osteochondrosis is a very common disease in the modern world. Many people have it in the early stages, but do not even suspect. Generalized neck osteochondrosis occurred due to the fact that people begin to sit more and move less. Let's take a look at the reasons for the development of this unpleasant disease and methods of combating it.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
Therefore, cervical osteochondrosis is a degenerative-distribution disease of the tissues of the musculoskeletal system cartilage. The disease is characterized by pathological changes in the cartilage structure, which leads to a violation of the anatomical structure of the spine elements, interrupts the mobility of the skeleton and causes painful sensations. The disease may affect any part of the spine, but due to excessive mobility and miniature vertebral size, the cervical segment suffers this pathology more often. The neck is going through impressive charges daily. Head turns and even the fact that its retention forces the vertebrae and intervertebral discs to function intensely. Since regular exposure outside, intervertebral discs are thinner, microcracks appear on them. Over time, their height decreases, they begin to change thickness in the smaller way and fail to fulfill their main function - depreciation of the vertebrae.
The causes of cervical osteochondrosis
The causes of disease development, first and foremost, are due to aging related to the age of the body and the destruction in the development of bones and cartilage. The following causes of osteochondrosis can also be called:
- Posture Violation
- Reduction of motor activity as a result of a sedentary lifestyle
- Overweight, which is the result of metabolic disorders, has a load on intervertebral discs
- Hereditary factor
- Long -term physical activity
- Column abnormalities
Cervical osteochondrosis symptoms
Cervical osteochondrosis has specific manifestations. This is due to the anatomical characteristics of the cervical spine. Most of the time, patients complain of pain of various intensity, increasing a long stay in a position. Other symptoms are often added to pain:
- weakness in the upper limbs
- Numbness and tingling
- rigidity when moving the head
- dizziness (suggests that damaged elements affected the arteries)
- Dormancy of the lips
- Feeling of a coma in the throat
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis
In medicine, it is usual to separate signs of osteochondrosis based on the nature of symptomatic manifestations combined in a single syndrome. 4 of these syndrome are distinguished:
- KORESHKA - Indicates compressed nerve beams, which cause serious pain, as well as a set of autonomic symptoms (dizziness, weakness, throat nodule);
- Vertebral artery - damaged elements arrest the large vertebral artery, which is the cause of serious headaches, dizziness;
- Vertebral - causes pain in the neck itself;
- CARDIAL - It is masked under an attack by Angina Pectoris, manifested by pain in the intense chest, similar to a heart attack.
Cervical osteochondrosis development stages
1 degree of osteochondrosis
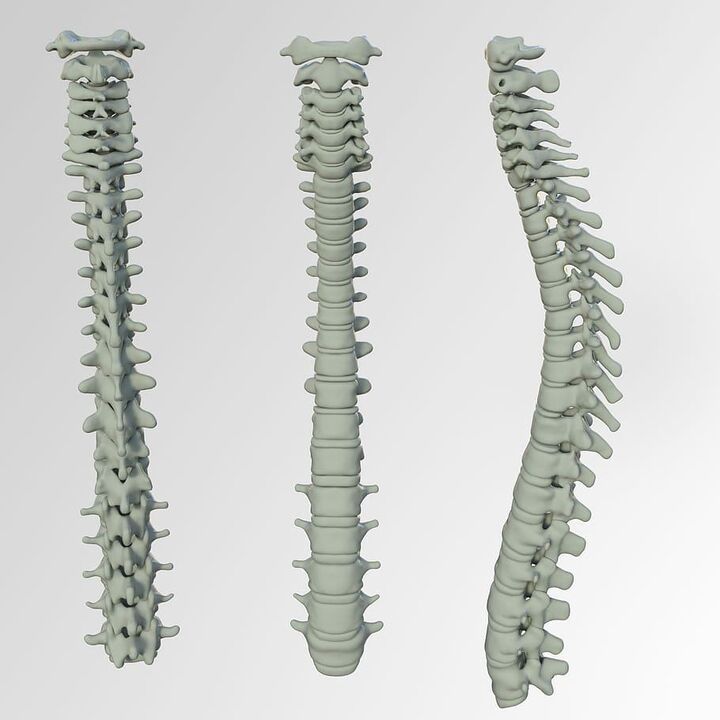
It is characterized by the beginning of the destruction of the intervertebral discs. Cracks are formed in the fibrous ring, the strength and elasticity of the disc are formed, their height decreases, because the nerve roots are squeezed. A painful pain characteristic appears. Sometimes, in 1 stage (pre -clinical), this pain may be absent, and osteochondrosis proceeds with moderate neck discomfort.
2 degree of osteochondrosis
If the 1st degree osteochondrosis was not treated or the treatment was not effective, the 2nd degree - chronic - chronic osteochondrosis occurs. The pain becomes constant, the destruction and seal of the intervertebral disc continues and lead to small dislocation of the cervical vertebrae. With cervical osteochondrosis, a falling head syndrome can develop at this stage. This syndrome is characterized by intense pain and a person is forced to support his head in a fixed state to reduce pain.
3 degree of osteochondrosis
The fibrous ring is almost destroyed, which leads to complications of osteochondrosis - intervertebral disk protrusion or intervertebral hernia. In three stages of osteochondrosis, the intensity of the pain may decrease, since the cartilaginous tissue affected on the disc between the vertebrae is no longer there, which means there is no source of pain, however, the pinch of nerve roots remains, so that the pain does not come out completely.
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
If it is suspected of the presence of cervical osteochondrosis, it is necessary to contact a timely medical institution. Comprehensive diagnosis will help identify the disease, evaluate its degree, and understand the causes of pathology development.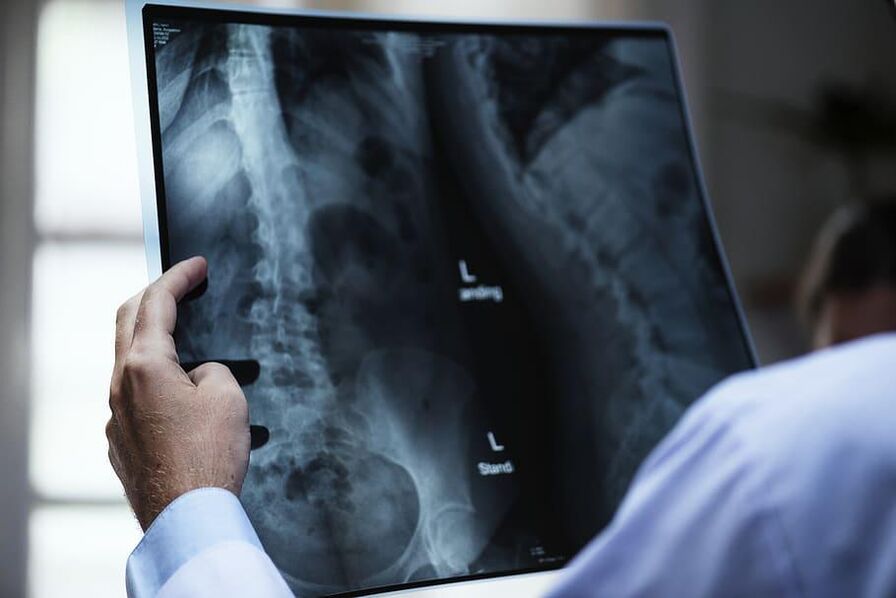 A preliminary diagnosis is based on inspection and palpation - with osteochondrosis, the tension of the cervical muscles is observed; In some cases, the deformation of the spine is noticeable. After the objective diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient to additional studies. The following diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
A preliminary diagnosis is based on inspection and palpation - with osteochondrosis, the tension of the cervical muscles is observed; In some cases, the deformation of the spine is noticeable. After the objective diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient to additional studies. The following diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Magnetic Resonance Tomography
- Radiography (lateral and straight)
- Computed tomography
To determine the cause of pathology development, an ultrasound examination of nearby organs, heart ECG, duplex scanning of blood vessels, blood and urine tests can be prescribed additionally.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The treatment of osteochondrosis requires an integrated approach. For the temporary elimination of pain, painkillers are used, but the basis of therapy is physiotherapy and massage. Massage helps relieve muscle hypertension by increasing pain. The procedures also restore normal blood circulation, improving the supply of damaged tissues. Based on the results of the massage course, the voltage is removed from the cervical region, the load in the spine is redistributed. Drug treatment. Drugs relieve pain and inflammation, restore blood circulation and eliminate cramps in the neck muscles. For this, the following groups of medications can be used: glucocosteroids, painkillers, muscle relaxants, etc. Physiotherapeutic treatment. In addition to taking drugs to relax near cervical muscles, eliminating cramps and normalizing blood circulation will help physiotherapeutic procedures: acupuncture, laser effect, magnetotherapy, UHF therapy, phonophoresis etc.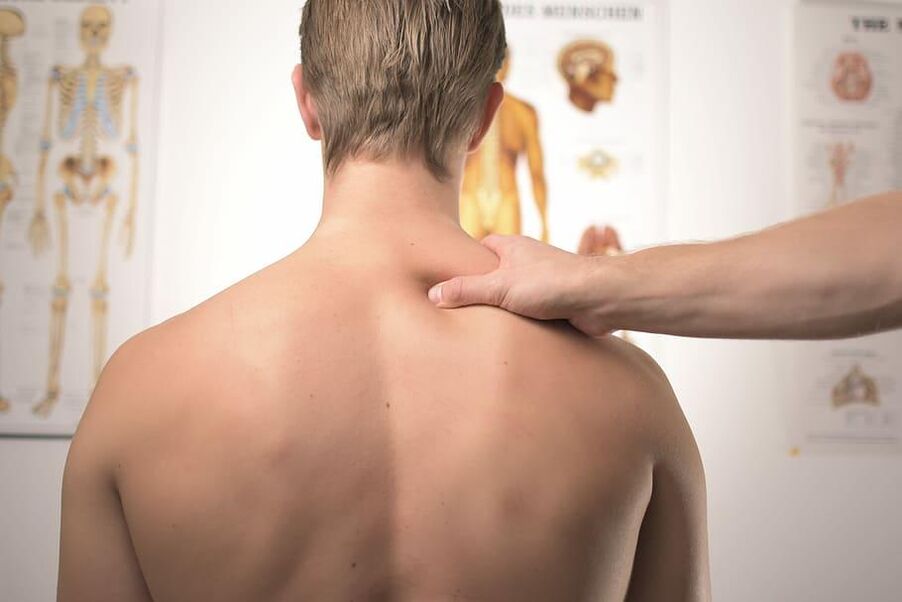 Therapeutic Gymnastics. Special exercise will help the patient strengthen muscle structure, align posture and improve blood supply to the top of the spine of the spine. In the case of advanced stages of cervical spine osteochondrosis or with insufficient effectiveness of conservative methods, surgery is required.
Therapeutic Gymnastics. Special exercise will help the patient strengthen muscle structure, align posture and improve blood supply to the top of the spine of the spine. In the case of advanced stages of cervical spine osteochondrosis or with insufficient effectiveness of conservative methods, surgery is required.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
To prevent the development of cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended: when sitting, make sure to make five -minute intervals every hour, avoid neck loads; Do not make clear movements of the head, monitor the posture; Avoid hypothermia; engage in physical education, swimming; eat properly; The dream must be in a solid mattress and a low pillow, the bending angle should not exceed 15 degrees; After 25 years, avoid the shock load in the spine (jumping, running). Anyway, when the symptoms of the disease appear - be sure to visit a doctor. Don't be self -like!













































